Variable Density sampling and Radial view-ordering (VDRad) MATLAB DEMO
For 3D Cartesian imaging, we focus the design of the data acquisition scheme on achieving motion-robustness and ideal undersampling patterns for accelerated imaging techniques. The technique that we have developed is the variable density sampling and radial view-ordering, VDRad for short. For more information, please see Ref. 1.
This DEMO creates the Fig. 9 shown in Ref. 1 using the VDRad sampling/ordering scheme. The goal of of this DEMO is to illustrate the flexiblity of the sampling pattern and ordering. The sampling patterns are designed for a 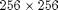 matrix. The main matlab function used to generate these example sampling patterns is vo_vdrad. For more details about specific parameters, see help vo_vdrad.
matrix. The main matlab function used to generate these example sampling patterns is vo_vdrad. For more details about specific parameters, see help vo_vdrad.
The VDRad scheme also has a temporal component. To see the temporal component, use the matlab function vo_drawordertrain. See the specific help descriptions for more details.
References:
- Cheng JY, Zhang T, Ruangwattanapaisarn N, Alley MT, Uecker M, Pauly JM, Lustig M, Vasanawala SS. Free-breathing pediatric imaging with nonrigid motion correction and acceleratedion. J Magn Reson Imaging 2014. Accepted Oct 6, 2014.
- Cheng JY, Zhang T, Alley MT, Lustig M, Vasanawala SS, Pauly JM. Variable-density radial view-ordering and sampling for time-optimized 3D Cartesian imaging. In Proceedings of the ISMRM Workshop on Data Sampling and Image Reconstruction, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, 2013.
- Winkelmann S, Schaeffter T, Koehler T, Eggers H, Doessel O. An optimal radial profile order based on the Golden Ratio for time-resolved MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2007; 26:68–76.
Return to software.
(c) Joseph Y. Cheng (jycheng@mrsrl.stanford.edu) 2013.
Contents
We first setup the library and a number of common parameters.
addpath mlib; % location of matlab functions fov = [300 300]; % field of view (in [mm]) msize = [256 256]; % matrix size tl = 24; % spoke train length ncal = 24; % calibration region diameter nph = 1; % number of temporal phases
Example 1: Elliptical sampling density
To generate an elliptical sampling density, the function for  is as follows:
is as follows:
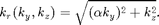
Setup parameters:
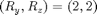
- corner cut = ON
- corner cut calib region = ON
param_a = {'type', 'ellipse',... % default
'corner', 1,... % default (corner cut ON)
'cornercal', 1,... % default (corner cut calib ON)
'spiral', 0,...
'demo', 1};
acc_a = [2 2];
[yo_a,zo_a] = vo_vdrad(fov,msize,acc_a,ncal,tl,nph,param_a);

Example 2: Elliptical sampling density with a spiral twist
Function for 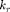 is the same as Example 1. To add the spiral twist, the following function for
is the same as Example 1. To add the spiral twist, the following function for 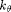 is used:
is used:
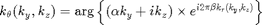
Setup parameters:
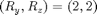
- corner cut = ON
- corner cut calib region = ON
param_b = {'type', 'ellipse',... % default
'corner', 1,... % default (corner cut ON)
'cornercal', 1,... % default (corner cut calib ON)
'spiral', 20,... % degree of spiral twist
'demo', 2};
acc_b = [2 2];
[yo_b,zo_b] = vo_vdrad(fov,msize,acc_b,ncal,tl,nph,param_b);

Example 3: Ellipitical sampling density (anisotropic) with a spiral twist
Function for 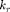 and
and 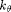 are the same as Example 1 and Example 2 respectively. Here, an anisotropic sampling density is used (
are the same as Example 1 and Example 2 respectively. Here, an anisotropic sampling density is used (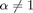 ).
).
Setup parameters:
- corner cut = ON
- corner cut calib region = ON
param_c = {'type', 'ellipse',... % default
'corner', 1,... % default (corner cut ON)
'cornercal', 1,... % default (corner cut calib ON)
'spiral', 20,...
'demo', 3};
acc_c = [4 2];
[yo_c,zo_c] = vo_vdrad(fov,msize,acc_c,ncal,tl,nph,param_c);

Example 4: Square sampling density (anisotropic)
To generate a square sampling density, the function for 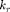 is as follows:
is as follows:
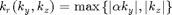
Setup parameters:
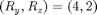
- corner cut = OFF
- corner cut calib region = OFF
param_d = {'type', 'square',...
'corner', 0,...
'cornercal', 0,...
'spiral', 0,...
'demo', 4};
acc_d = [4 2];
tl_d = 23; % change spoke number for aesthetic reasons
[yo_d,zo_d] = vo_vdrad(fov,msize,acc_d,ncal,tl_d,nph,param_d);

Example 5: Triangle sampling density (anisotropic)
To generate a triangle sampling density (separable sampling density), the function for 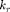 is as follows:
is as follows:
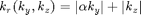
Setup parameters:
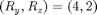
- corner cut = OFF
- corner cut calib region = OFF
param_e = {'type', 'triangle',...
'corner', 0,...
'cornercal', 0,...
'spiral', 0,...
'demo', 5};
acc_e = [4 2];
tl_e = 23; % change spoke number for aesthetic reasons
[yo_e,zo_e] = vo_vdrad(fov,msize,acc_e,ncal,tl_e,nph,param_e);

About
This DEMO is for illustration purposes only. Please let me know if you have suggestions or see any errors/bugs. Thanks!
- Author: Joseph Y. Cheng (jycheng@mrsrl.stanford.edu)
- Version: 0.2
disp(sprintf('This DEMO was generated on %s.',date));
This DEMO was generated on 16-Oct-2014.